Abstract : In this paper, through the introduction of the biodegradability and shape temperature control memory mechanism of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL), the molding process of some poly(hexyl-hexyl ester) polymer materials is analyzed at the same time. The products are used in the medical, daily and agricultural industries. Finally, the application prospects of using special processing technology to build new polycaprolactones are prospected. Keywords: polycaprolactone degradability memory process Since the 1960s, PCL polycaprolacton has received extensive attention due to its superior biodegradability and memory, and its related research has also been rapidly developed. PCL is a semi-crystalline polymer having a melting point of 59-64°C and a glass transition temperature of -60°C. The structure repeat unit has five non-polar methylene-CH2?CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2-) P n , such structure makes PCL have very good flexibility and processability, and the material has very good biocompatibility. Sex. This structural feature, on the one hand, enables it to have a shape memory property, an article having an initial shape, which can be restored to its original shape after being deformed and fixed by heat and other external conditions. On the other hand, the material is blended with starch and other materials to produce a completely biodegradable material. At present, these two characteristics have been applied in many fields, especially in the medical field, such as tapes, bandages, orthotics, sutures, drug release agents, and the like. - and a polar ester group -coo-, that is - (COO-CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 -) Pn, this structure makes PCL has good flexibility and processability, and this material has good biocompatibility . This structural feature, on the one hand, enables it to have a shape memory property, an article having an initial shape, which can be restored to its original shape after being deformed and fixed by heat and other external conditions. On the other hand, the material is blended with starch and other materials to produce a completely biodegradable material. At present, these two characteristics have been applied in many fields, especially in the medical field, such as tapes, bandages, orthotics, sutures, drug release agents, and the like. <> 1. The characteristics of polycaprolactone 1.1 Degradation mechanism Polycaprolactone is a chemically synthesized biodegradable polymer material. Its molecular structure incorporates an ester-based structure, coo-. In nature, the ester-based structure is easily decomposed by microorganisms or enzymes. The final products are CO2 and H2O. [1]: The specific process is as follows: The first stage: hydration. The material absorbs water from the surrounding environment. This process takes several days or months, depending on the material's properties and surface area. The second stage: The main chain of the polymer breaks chemical chains due to hydrolysis or enzymatic hydrolysis, resulting in a decrease in molecular weight and mechanical properties. The third stage: After the loss of strength, the polymer becomes an oligomer fragment, and the overall quality begins to decrease. Stage 4: The oligomers are further hydrolyzed into smaller fragments that are absorbed by phagocytic cells or further hydrolyzed to produce CO2 and H2O. According to relevant materials, PCL products with a molecular weight of 30,000 disappeared in soil after one year, and PCL was therefore recommended as an “environmentally friendly†packaging material. 1.2 The mechanism of shape memory The shape-memory function of high-molecular polycaprolactone (PCL) material mainly comes from the incompletely compatible two phases in the material: the stationary phase that maintains the shape of the molded article and the softening that changes with the temperature—the reversible change of hardening reversible. . The reversible phase, such as the lower crystalline state of the lower melting point (Tm) or the lower glass state of the glass transition temperature (Tg), has a physically cross-linked structure. The stationary phase may have a physically cross-linked structure (such as a molecular twist formed by a phase having a relatively high Tm or Tg at a lower temperature), and may also have a chemically cross-linked structure. The stationary phase and the reversible phase have different softening temperatures (identified as Ta and Tb, respectively). In a single molding process, the material is heated to above Ta, and both the stationary phase and the reversible phase are in a softened state. After cooling to below Tb, the stationary phase and the reversible phase are hardened successively and the material is formed. Overmolding is to heat the molding material to the softening temperature of the reversible phase (Tb In the formula, L-sample original length; △ L-shaped variable. At present, for the PCL shape memory materials, Japan Yamaguchi put forward a more appropriate interpretation of the mechanical model. He believes that [6] the deformation rate of rubber-like shape memory material under the action of external force σ consists of three parts, namely instantaneous deformation rate ε0, relaxation deformation rate εr and creep deformation rate εc: ε = ε0 + εr + εc After the external force is released, the instantaneous deformed rate recovery εc′ and creep deformation variability recovery εc′ occur when the deformed state that has been solidified is heated. Since the relaxation deformation rate εr is a plastic deformation, the deformation rate recovery εr′ is extremely small, but when heated to the shape recovery temperature, εr Deformation rate recovery εn′ occurs. At this point, the material is restored to its original shape on a macroscopic level. 2. Modification of polycaprolactone [7] Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a product developed by DICELL Chemical Industry. The material has a molecular weight of 40,000, a melting point of 59-64°C, a glass transition temperature of -60°C, an orthopaedic temperature of 60-70°C, and a decomposition temperature of 200°C. The melting point and the decomposition temperature thereof are relatively low and are not suitable for general use. Plastic molding process. In addition, the flexibility of the structure is insufficient as a bracket for orthopedics. Therefore, it is necessary to modify the PCL. By modifying the PCL, a variety of new polycaprolactones that can adapt to existing (or improved processing technology requirements and can achieve specific functional requirements) are constructed. The current modification routes are mainly 1PCL/TDL/BDO polyurethane systems, which are hydroxyl-terminated polycaprolactone (PCL), 2,4-toluene diisocyanate (2,4-TDI), chain extender 1,4 A multi-block polyurethane sample was prepared using 2-butyrodiol (BDO) as the raw material, in which the PCL was a soft segment and the TDI-BDO was a hard segment; 2PCL/MDI/BDO system, diphenylmethane diisocyanate ( MDI) is the chain extension system, PCL is a soft segment, and MDI/BDO is a hard segment. 3PCL/isopropylideneacetone (IPDI) 12-hydroxyxylylene acrylate system.
Press material can be divided into aluminum pressure cooker pressure cooker and stainless steel pressure cooker. Press the lid can be divided into screw type, cover type gland and fall. The most common on the market as a spin-fit.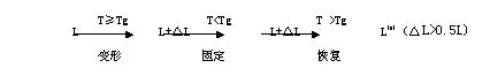
Pressure cooker in accordance with national standards GB13623 -92 and GB15066-94 requirements must be provided with three security devices: pressure limiting devices, safety pressure protection device and opening and closing the lid pressure protection device.
Cooking with wok best.
All kinds of pot
Various pot
Wipe.
Or wok well. Pollution, uniform heating. Chefs are using wok.
Wok: currently the safest pot
World Health Organization experts began to recommend the use of the wok, wok is a traditional kitchen, generally do not contain other chemicals, it is not oxidized.
Magnetic Compound Bottom Pot,Magnetic Induction Cookware,Induction Bottom Pots,Magnetic Cooking Pans
ChuangHengDa Stainless Steel Company , http://www.nbcookwares.com