3 Effect of Printing Materials on Network Changes 4 Effect of Ink Type on Dot Change 5 Effect of Exposure Time on Dot Change Conclusion <br> This article from the factors that affect the color screen printing dot changes in various factors, the color screen printing dot changes in the experimental analysis, in order to obtain a set of color screen printing for the separation of color provides a certain reference in accordance with. The conclusions of this experiment are summarized as follows: (1) Color tone screen printing. The number of screen lines is not as high as possible. It is recommended that the ratio of the screen mesh number to the screen number be 5 to 6. (2) In screen printing, the effect of dot gain on printed matter is much greater than that caused by dot loss. Therefore, when color screening is performed, it is recommended to use chain-shaped dots and square dots. (3) When the other conditions are determined, the color of the screen should be determined according to the printing materials, and the coarse surface resolution is low. Therefore, a thicker screen cable is used instead of a fine screen cable; the absorptive surface is enlarged. Small, network cable should be fine, otherwise it is thick. (4) From the experiments we know that color tone screen printing loses the bright tone and increases the tone value of the tone. Therefore, in order to achieve accurate reproduction of the tone, it is recommended to do a correction of the tone during color separation, for example, : Want to completely copy out the 5% to 95% of the tone, we first make a tone sheet of 15% to 85% of the original, when made into screen printing, 15% of the network will To 5%, 85% of outlets will increase to 95%, so that complete reproduction of the tone can be achieved. Wooden Whiteboard,Dry Erase Boards,School Writing Board Xindi Rubber Products Factory , http://www.sofine-board.com
Experiment 3 Printing was performed using the same type of ink, the same number of lines, the same exposure time, the same dot shape, and different substrates (silk screen printing ink, 40 lpi, exposure time 40 seconds, square dots, art paper, and offset paper). 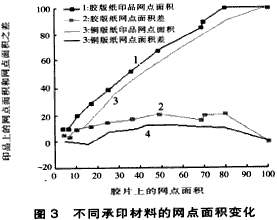
From the dot change curve of experiment 3 (Figure 3), it can be seen that the dot enlargement on the offset paper is larger than the dot enlargement on the copperplate paper, and we know that the silkscreen ink dries quickly, while the offset paper surface is rough, and the absorption is strong, resulting in the dot Expansion is much smaller than coated paper. Obviously, the experimental results are inconsistent with this, which is mainly due to the influence of improper control of some tiny links in the printing process, such as the squeegee pressure, the squeegee angle, and the speed of squeegee printing.
Experiment 4 Printing was performed using the same number of lines, the same exposure time, the same substrate, and different types of ink (40 lpi, 40 s, square dot, coated paper, yellow ink in offset printing, screen printing green ink). 
From the dot change curve of experiment 4 (Fig. 4), it can be seen that dot gain caused by offset ink printing is smaller than dot gain caused by screen printing ink printing, and we know that the viscosity of silk screen ink is generally higher than the viscosity of offset ink in general. The dot gain produced is smaller than that of offset printing, but dot gain caused by the thicker ink layer of screen printing ink predominates, resulting in even more dot gain caused by screen printing ink printing.
Experiment 5 Using the same number of lines, the same substrate, the same exposure time for different types of ink, printing (40 lpi, 30s and 50s, square dots, coated paper, yellow ink in offset printing).
From the dot change curve of experiment 5 (FIG. 5), it can be seen that the exposure time is long and the dot gain value is small, but the tone loss of the highlight part is severe. In this experiment, when the exposure time was 50 s, almost all of the dots below 10% were lost. 