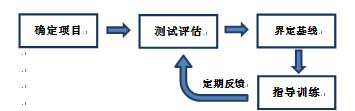
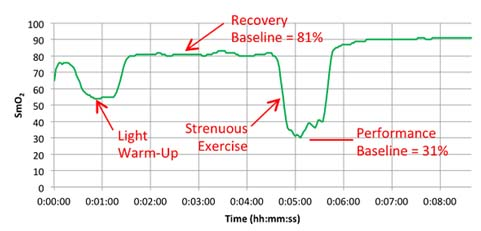
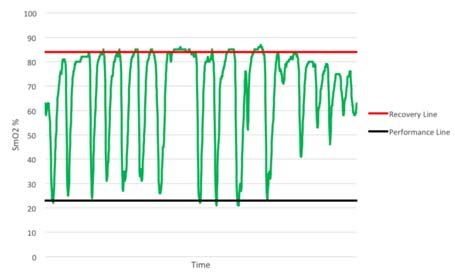
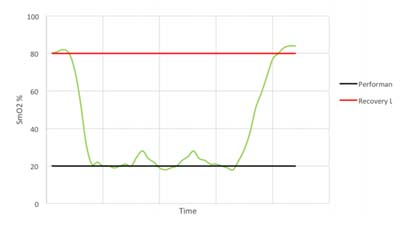
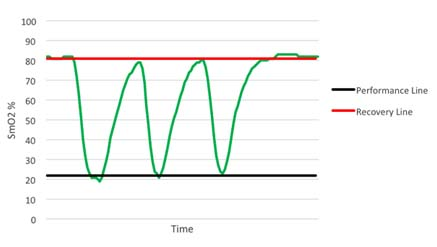
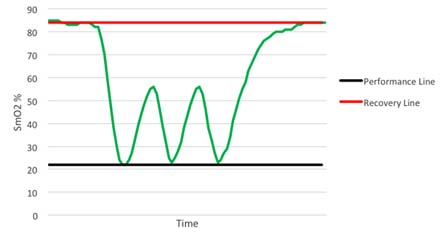
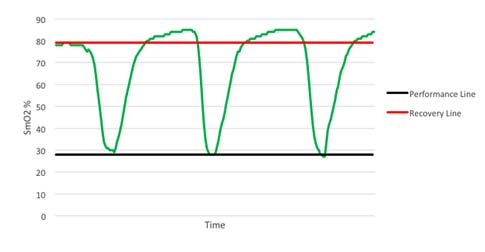
First, the introduction Myotrope monitoring technology provides real-time physiological feedback on the relationship between muscle oxygen consumption and oxygen supply. The relationship between muscle oxygen consumption and oxygen supply is a determinant of muscle recovery and fatigue levels, so it can be used to guide the number of repetitions of strength training, the number of groups, and the time between groups to achieve optimal training results. If the goal of training is muscle thickening, then the required muscle physiological adaptability should be the improvement of maximum muscle strength or muscle endurance, and providing training guidance based on individualized physiological parameters can most effectively achieve this muscle adaptation. Second, the guiding process Use muscle oxygen monitoring indicators to guide strength training flowchart 1, determine the project According to the training objectives, the trainee is determined to participate in the project. 2, test evaluation The purpose of the test is to determine the muscle oxygen function partition and load intensity of the trainee in the exercise program, and to develop a later training plan. Therefore, the test plan should be as consistent as possible with the actual training. This article takes biceps training as an example to illustrate. 3. Define the baseline The figure below shows how to determine the baseline of baseline recovery and exercise capacity of the biceps during one-armed curling. The light warm body is composed of 25 4 pound weights. The high-intensity training consists of 25 17-pound weights. Determine the muscle oxygen line during biceps flexion The figure below shows the data of 15 groups of strength training. In each group, repeat the action until you reach a low platform. Groups 1-3 show a low platform to reach the baseline of exercise capacity. Groups 4-7 show a low platform that is slightly above the baseline of athletic ability. Groups 8-11 show a low platform that has experienced a longer recovery period and once again reached the baseline of athletic ability. The last four groups show that the athletes are no longer able to approach the baseline of athletic ability and cannot return to the baseline of recovery. Determine the muscle oxygen line during biceps flexion After the Recovery Line and the Performance Line were established, training began. However, before starting, the main training objectives must be determined. Is muscle hypertrophy, maximum muscle strength, or muscle endurance? 4. Guided training Different training purposes are used to train with different recovery principles. Hypoxia recovery principle (no complete recovery or extension of exercise time per group) The purpose of hypoxia recovery is to prevent significant recovery of SmO2 (see figure below). In order to achieve this, each group needs to move for a longer period of time and recover in a shorter time. It can be achieved in the following ways. The first one can be repeated multiple times using the second maximum load, repeated for a long time until exhaustion. Second, the maximum load motion can be followed by low-load training to increase the number of weights (traditionally referred to as descending training). Third, the training time can be verified by slowing down the speed of movement in each movement or by stopping the isometric contraction during exercise. After completing this extended group, SmO2 should be restored to the baseline value. Then start the next group immediately. Characteristics of muscle oxygen changes under the principle of hypoxia recovery a. Complete recovery principle The goal of full recovery is to return SmO2 to a stable value or restore the baseline before the next set of movements begins (see figure below). The first step is to establish a recovery baseline SmO2 and then begin a set of exercises until the minimum SmO2 value or athletic ability baseline is reached. The next step is to rest until SmO2 reaches a steady value or restores the baseline. At this point, the next set of exercises begins and continues. Characteristics of muscle oxygen changes under the principle of complete recovery b. Incomplete recovery principle In the principle of incomplete recovery, SmO2 can never reach the recovery baseline, which is different from the principle of full recovery. But it is the same as the principle of full recovery, which is to establish a recovery baseline after a short warm-up exercise. Then start the first group until SmO2 reaches a minimum and establish a baseline of athletic ability. After the end of the first group, only a limited recovery time is scheduled and then the next set is started. The determination of the recovery time depends on a number of factors, such as the sporting goal or the type of competition. In the example below (see Figure 5), the limited recovery time is equal to the time at which SmO2 reaches the midpoint of the baseline of recovery and baseline of athletic ability. Then start the second group. Characteristics of muscle oxygen changes under the principle of incomplete recovery c. Excess recovery principle The purpose of over recovery is to allow SmO2 to reach data above the maximum between groups. This value typically exceeds the baseline of recovery due to increased cardiac output and increased vasodilation in the motor muscles. The following example (see Figure 6) shows that SmO2 recovery exceeds the recovery baseline until the platform period is reached, and then the next set of motions begins. Characteristics of muscle oxygen changes under the principle of excess recovery After familiarizing with these principles of recovery, it is necessary to conduct targeted muscle training through these principles. 1) Muscle hypertrophy training Muscle hypertrophy training aims to increase muscle volume. The increase in muscle volume can be promoted by the level of auxin naturally secreted by the body under the intensity of anaerobic training. The number of repetitions of this training is determined by the speed of each movement and the duration of the muscle's anaerobic intensity (eg, low muscle oxygen value). Each movement should meet the specified range of joint mobility and be controlled during flexion and extension. The goal of the following training case is to keep SmO2 at a minimum, thus extending the duration of training intensity based on the full recovery principle. This will combine the two principles of hypoxia recovery and full recovery. Training example Ø Select a weight for the target muscle according to the baseline of exercise ability, and increase the number of training groups to 5 groups. Ø Adopt the principle of hypoxia recovery at the 3rd to 5th hour. That is, the level of SmO2 is maintained at the baseline of exercise capacity for 15 seconds. Ø The principle of complete recovery is adopted between the groups. The use of a descending training program is very effective. Using a large intensity to quickly reduce the level of SmO2 and then using a lighter weight for a long time is to keep SmO2 at the baseline of exercise capacity, which is very effective for muscle hypertrophy. 2) Maximum muscle strength and explosive training The purpose of maximum muscle strength and explosive training is to increase the maximum force or explosive force generated by one or several movements. Both of these need to be the muscles that can get the most energy supply to produce maximum contraction strength. The use of the excess recovery principle between each group can provide time for the recovery of the energy consumption pathway. The number of repetitions of this type of training is determined by the ability to reproduce the maximum force, so the number of repetitions is generally small. Each movement of maximum muscle strength training should meet the specified range of joint motion, and should be controlled slowly and slowly; on the other hand, the maximum explosive force training should complete each action explosively. Training example – maximum explosive training: • Complete a series of the biggest explosive knee-high jumps until exhaustion (do your best). • Complete the over recovery of SmO2 and start the second group. • The number of repeated target groups is when the SmO2 level cannot be restored to the exercise capacity baseline or the baseline is restored, or straight Carry out other training. Training example Ø Complete a series of maximum muscle repetitive movements for a given training (low repetitions 1-4 times, maximum exertion). Ø Complete SmO2 over recovery and start the second group. Ø The number of repeated target groups is when the SmO2 level cannot be restored to the exercise capacity baseline or the baseline is restored, or other training is directly performed. 3) Muscle endurance training Muscle endurance training is very different from maximum strength training. The goal of muscle endurance training is to perform long-term sustained muscle contraction at a given level of ability rather than maximizing exertion. The continuous supply of energy during contraction constitutes the endurance of the muscle. To this end, we propose to combine the principle of full recovery with the principle of incomplete recovery. First, as with muscle hypertrophy training, this method first promotes blood vessels in the hypoxic environment to increase oxygen transport to the working muscles. Then, the muscles are required to have sufficient endurance to maintain the requirement of continuous contraction. Muscle endurance training uses a large number of repetitions to exhaustive submaximal intensity loads. The number of repetitions depends on the speed of each iteration. Each movement must meet the specified range of joint motion and be controlled. The following training case combines the principle of full recovery with the principle of incomplete recovery. Training example Ø Complete a series of actions at 40-50% intensity of 1RM until exhaustion. Note that this load is completed at least 10 times, otherwise a lower weight is used. Ø Rest according to the SmO2 full recovery principle, then start the second group. Ø The goal of each group is to repeat the same number of repetitions (the number of times that can be exhausted). If the number of repetitions is significantly reduced, then a lower weight is chosen to ensure adequate duration of exercise. Ø Number of repeats: When SmO2 can no longer reach the capacity baseline and/or restore baseline during the break between groups The number of groups in Ø. Ø The principle of recovery can be periodically changed to the principle of incomplete recovery to change physiological adaptation. Foot File Very Simple And Helpful Double Sided Foot File,Foot Callus Remover Tool,Pedicure Tools,Foot Scraper For Dead Skin SZ CHENGYANG BEAUTY TOOLS CO.,LTD , https://www.cyfootfile.com